Mechanical Vision
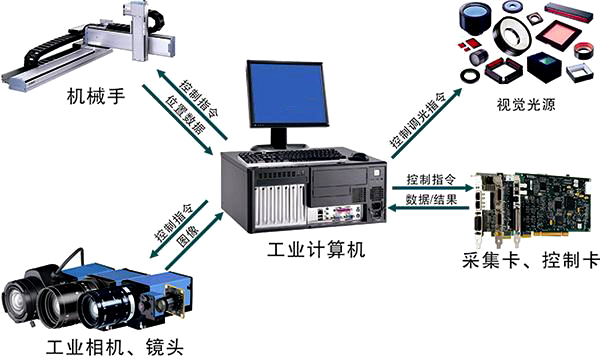
Machine Vision is a comprehensive technology that includes image processing, mechanical engineering, control, electric light source illumination, optical imaging, sensors, simulation and Digital video technology, computer hardware and software technology (image enhancement and analysis algorithms, image cards, I/O cards, etc.). A typical machine vision application system includes image capture, light source system, image digitization module, digital image processing module, intelligent judgment decision module and mechanical control execution module.
How it works
The machine vision inspection system uses a CCD camera to convert the detected object into an image signal, which is transmitted to a dedicated image processing system and transformed according to pixel distribution and brightness, color and other information. Digital signal, the image processing system performs various operations on these signals to extract the characteristics of the target, such as area, quantity, position, length, and then output the result according to the preset allowable degree and other conditions, including size, angle, number, Qualified / unqualified, with / without, to achieve automatic identification.
Applications
The application of machine vision mainly has two aspects of detection and robot vision:
1. Detection: It can be divided into high-precision quantitative detection (such as cell classification of micrographs, size and position measurement of mechanical parts) and qualitative or Semi-quantitative testing (eg visual inspection of products, component identification positioning on assembly lines, defect detection and assembly integrity testing).
2. Robot Vision: Used to guide the robot's operations and actions on a wide range, such as picking up the workpiece from a messy pile of hoppers and placing it in a certain orientation On a conveyor belt or other equipment (ie, hopper picking problems). As for operations and actions in a small area, it is also necessary to resort to tactile sensing technology.